Electronic Coupling between Two Amine Redox Sites through the 5,5′-Positions of Metal-Chelating 2,2′-Bipyridines
Nie, H.-J., Chen, X., Yao, C.-J., Zhong, Y.-W., Hutchison, G. R. and Yao, J. “Electronic Coupling between Two Amine Redox Sites through the 5,5′-Positions of Metal-Chelating 2,2′-Bipyridines” Chem. Eur. J. 2012 18(45) pp. 14497–14509. Online. The supplemental info is available here: Nie SI.
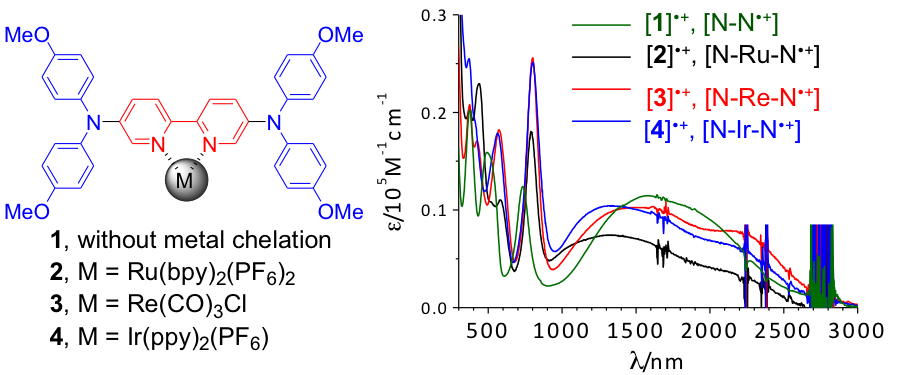 Electron delocalization of new mixed-valent (MV) systems with the aid of lateral metal chelation is reported. 2,2′-Bipyridine (bpy) derivatives with one or two appended di-_p_-anisylamino groups on the 5,5′-positions and a coordinated [Ru(bpy)2] (bpy=2,2′-bipyridine), [Re(CO)3Cl], or [Ir(ppy)2] (ppy=2-phenylpyridine) component were prepared. The single-crystal molecular structure of the bis-amine ligand without metal chelation is presented. The electronic properties of these complexes were studied and compared by electrochemical and spectroscopic techniques and DFT/TDDFT calculations. Compounds with two di-_p_-anisylamino groups were oxidized by a chemical or electrochemical method and monitored by near-infrared (NIR) absorption spectral changes. Marcus–Hush analysis of the resulting intervalence charge-transfer transitions indicated that electron coupling of these mixed-valent systems is enhanced by metal chelation and that the iridium complex has the largest coupling. TDDFT calculations were employed to interpret the NIR transitions of these MV systems.
Electron delocalization of new mixed-valent (MV) systems with the aid of lateral metal chelation is reported. 2,2′-Bipyridine (bpy) derivatives with one or two appended di-_p_-anisylamino groups on the 5,5′-positions and a coordinated [Ru(bpy)2] (bpy=2,2′-bipyridine), [Re(CO)3Cl], or [Ir(ppy)2] (ppy=2-phenylpyridine) component were prepared. The single-crystal molecular structure of the bis-amine ligand without metal chelation is presented. The electronic properties of these complexes were studied and compared by electrochemical and spectroscopic techniques and DFT/TDDFT calculations. Compounds with two di-_p_-anisylamino groups were oxidized by a chemical or electrochemical method and monitored by near-infrared (NIR) absorption spectral changes. Marcus–Hush analysis of the resulting intervalence charge-transfer transitions indicated that electron coupling of these mixed-valent systems is enhanced by metal chelation and that the iridium complex has the largest coupling. TDDFT calculations were employed to interpret the NIR transitions of these MV systems.